XPS – X-ray Photoelectron spectroscopy
XPS in a nutshell
Category:
Qualitative chemical identity at the surface
Information about:
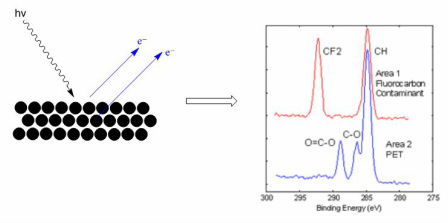
XPS is a non-destructive technique to measure surface chemistry of solid materials, in particular the chemical composition and electronic state.
Additional information:
XPS provides spatial resolution in the mm to µm regime, and depths of < 10 nm, and derives empirical formulae, binding energy, oxidation state, bond/electronic structure data.
XPS gives better resolution for heavier elements, particularly inorganic trace impurities of the bulk.
Measurements on:
Principally inorganic based materials, to determine composition and qualify level of impurities present and their binding affinity.
Application fields:
XPS is well suited for use in quality management and examination of surface chemical modifications to many material substrates including
Metallurgy: alloys, semiconductors, catalysts
Bio-materials: teeth, bones, wood composites, & medical implants
Polymers: plastics, coatings, impregnated inks
Plastic: surface modifier, additives, adhesion
Others: Paper, ceramics, glass, textiles
Expertise level:
Award winning knowledge transfer and innovation service provider.
Alternatives:
Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) or Photoemission Spectroscopy (PES) provide insights to the binding energy however they are less well suited to determine chemical composition across the sample. Elemental analysis (EA) of crushed samples is an alternative method to obtain empirical formulae, however exclusively of organic based samples.
Service Provider:
several providers at different locations
Description in Wikipedia:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_photoelectron_spectroscopy
Qualitative chemical identity at the surface
Information about:
XPS is a non-destructive technique to measure surface chemistry of solid materials, in particular the chemical composition and electronic state.
Additional information:
XPS provides spatial resolution in the mm to µm regime, and depths of < 10 nm, and derives empirical formulae, binding energy, oxidation state, bond/electronic structure data.
XPS gives better resolution for heavier elements, particularly inorganic trace impurities of the bulk.
Measurements on:
Principally inorganic based materials, to determine composition and qualify level of impurities present and their binding affinity.
Application fields:
XPS is well suited for use in quality management and examination of surface chemical modifications to many material substrates including
Metallurgy: alloys, semiconductors, catalysts
Bio-materials: teeth, bones, wood composites, & medical implants
Polymers: plastics, coatings, impregnated inks
Plastic: surface modifier, additives, adhesion
Others: Paper, ceramics, glass, textiles
Expertise level:
Award winning knowledge transfer and innovation service provider.
Alternatives:
Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) or Photoemission Spectroscopy (PES) provide insights to the binding energy however they are less well suited to determine chemical composition across the sample. Elemental analysis (EA) of crushed samples is an alternative method to obtain empirical formulae, however exclusively of organic based samples.
Service Provider:
several providers at different locations
Description in Wikipedia:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_photoelectron_spectroscopy

This is one of the methods that we can offer you to analyse your objects.
Please contact us for further details or an offer for your case.
Please contact us for further details or an offer for your case.